How Accurate is Optomap Retinal Imaging?
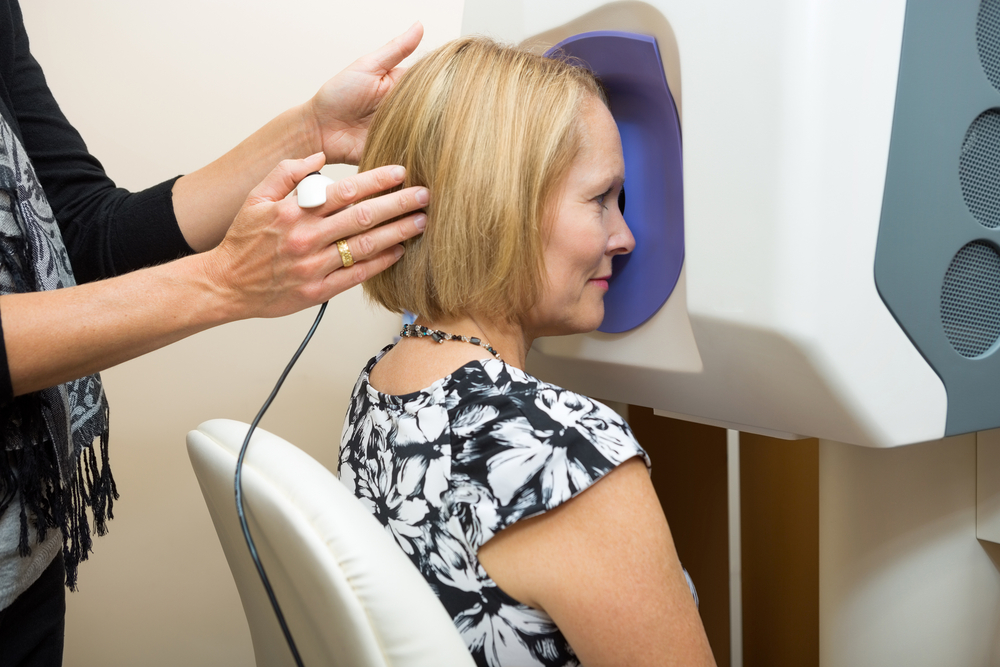
Optomap is a type of OCT or optical coherence tomography scan. These advanced scans use a special type of light to capture a 3D image that shows a cross-section of the different layers of the eye. This enhanced screening enables your eye doctor to visualize key areas of the eye with superior detail – something that makes detecting and diagnosing eye diseases much faster and easier. The sooner eye health problems are detected, the more likely your eye doctor is to be able to recommend treatment that will prolong your eye health.
Who Would Benefit From OTC?
OCT scanning can benefit all patients. However, it is particularly recommended for patients who:
Are over the age of 60
Have particular symptoms indicative of eye health issues
Have a family history of macular problems
Have an increased risk of glaucoma
How Accurate is Optomap Retinal Imaging?
Optomap retinal exams capture more than 80% of your retina in a single, panoramic image that takes a fraction of a second. This is more than any other current imaging technology, where approximately just 15% of the retina can be viewed. This is because Optomap uses a special light that enables your eye doctor to see deep into the periphery of your eye, visualizing those areas which are usually hard or impossible to see.
The images that are taken during Optomapping are stored digitally. Not only does this enable them to be reviewed immediately, but they can also be referred to in the future so that your eye doctor can monitor your eye health, including any developing problems, and intervene if and when necessary.
Optomap retinal imaging is considered to be one of the most accurate methods of retinal screening currently available.
Does Optomap Retinal Imaging Hurt?
One of the biggest concerns that many patients have about any sort of eye exam is that it will be painful. Fortunately, Optomap scans are completely non-invasive and don’t cause any discomfort. You’ll also be able to leave your appointment and go about your usual activities straight away, with no downtime as your eyes don’t need to recover.
Will I Need Pupil Dilation for Optomap Scanning?
Many types of eye scans require your pupils to be dilated so that your eye doctor can see through them and carry out a detailed assessment of the structures inside and at the back of your eye. However, it can take between 30 and 40 minutes for dilating eye drops to take effect, meaning that your appointment can take much longer than if you were to have screening using Optomap. It’s also important to note that it can take between 4 and 6 hours for your vision to return to normal after dilation and may remain blurred and unfocused during this time.
For more information call University Optometric Center in Irvine or Newport Beach, California at (949) 216-8900 or (949) 476-2870.